
Introduction
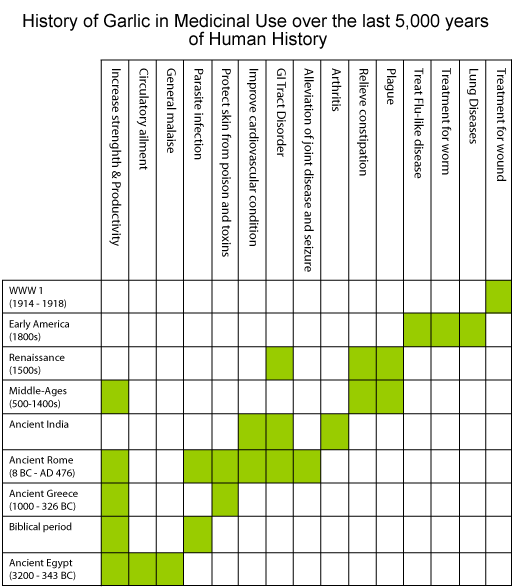
One of the earliest documented plants use by human for the treatment of diseases and maintenance of health was the garlic. Garlic was use at the beginning of recorded history and was found in Egyptian pyramids and ancient Greek temples. There are Biblical references to garlic. Ancient medical texts from Egypt, Greece, Rome, China and India each prescribed medical applications for garlic.
Cultures/civilizations that never came in contact with one another came to many of the same conclusions about the role of garlic in the treatment of diseases.Indeed, as you will soon find out, cultures/civilizations that never came in contact with one another, can fascinatingly, came to many of the same conclusions about the role of garlic in the treatment of diseases. Garlic was use for labourers for it was believed to be able to help improve their work capacity. Garlic was also recommended for pulmonary and respiratory complaints. Its efficacy in treating dropsy is compatible with known cardiovascular treatments.
Modern science is tending to confirm many of the beliefs of ancient cultures regarding garlic, defining mechanisms of action and exploring garlic’s potential for disease prevention and treatment.
Garlic in medical use: A historical perspective

- Garlic as part of the daily diet, particularly for the working class involved in heavy labour, as it was presumed to maintain and increase strength and productivity.
- The authoritative medical text of the era, the Codex Ebers, prescribed garlic for the treatment of abnormal growths. The Codex also prescribed garlic for circulatory ailments, general malaise and infestations with insects and parasites..
- Well-preserved garlic cloves were found in the tomb of King Tutankhamen who ruled from 1334 BC to 1325 BC.

- The Jewish slaves were fed garlic to maintain and increase strength and productivity, as it was believed to do so for the indigenous Egyptian citizens.
- On leaving Egypt, slaves were quoted to have missed their “fish, cucumbers, melons, leeks, onions and garlic”.
- The Talmud, a Jewish religious text dating from the 2nd century AD, prescribes garlic for the treatment of infection with parasites and other disorders.

- Soldiers were fed garlic to provide them with more courage, and garlic was part of the military’s daily diet.
- During the first Olympic Games, garlic was taken by athletes before they competed presumably to enhance performance.
- Garlic was used to protect the skin against poisons or toxins.
- Hippocrates, the Father of Medicine, used garlic as part of his therapeutic armamentarium, advocating its use for pulmonary complaints, as a cleansing or purgative agent, and for abdominal growths.

- The chief physician of Nero’s army recommended garlic to “clean the arteries” i.e. use garlic to improve cardiovascular status (The circulation of blood was not discovered until hundred years later).
- Garlic was also recommended for gastrointestinal tract disorder, treatment of animal bites and for alleviation of joint disease and seizures.
- In the five-volume Historica Naturalis (a medicine reference book), twenty-three uses of garlic was listed for a variety of disorder which includes protection against toxins and infections (a finding corroborated by contemporary investigations of the effects of garlic upon activities of P450-2E1) and other hepatic degradative diseases.
- Later, garlic was used for respiratory ailments and for parasites.

- Garlic was used as a food preservative.
- Formed part of the daily diet with raw meat.
- Garlic was prescribed to aid respiration and digestion, diarrhea and worm infestation.
- Garlic was prescribed was prescribed to lift depression.
- Garlic may have been used to improve male potency.

- Garlic has been associated with the healing process in India from the time of the first available written records.
- In the medical text named Charaka-Samhita, garlic was used to treat heart disease and arthritis.
- In another ancient medical text, known as the Bower manuscript (named after its discoverer), garlic was used for fatigue, parasites, digestive diseases and leprosy
- Medicinal use of garlic was featured prominently in The Hortulus manuscript, a leading medical reference text in that time.
- Garlic was believed to alleviate constipation when consumed with beverages.
- Workers outdoors were advised to consume garlic to prevent heat strokes (a recurring theme for those who were involved in hard physical labour).
- The medical school of Salerno taught dietetics to utilize garlic prominently.
- Garlic was used as a treatment for the great Plagues.

- Garlic was one of the major plants grown in the “Physic” gardens in leading universities for medical research purposes.
- A leading physician of the 16th Century, Dr. Pietro Mattioli of Siena, prescribed garlic for digestive disorders, kidney stones and expelling afterbirth.
- The English included garlic in their medicine chests, and it was used for toothache, constipation, dropsy and plague.

- Native Americans used garlic in a tea to treat flu-like symptoms.
- Garlic was used in Shaker herb catalogs as a stimulant, expectorant and tonic (1825).
- Dr. John Gunn used garlic in the book “Home: Book of Health” as a diuretic, expectorant and treatment for worms (1878).
- Dr. Joseph Richardson, author of Health Remedies, used garlic for all lung diseases.
